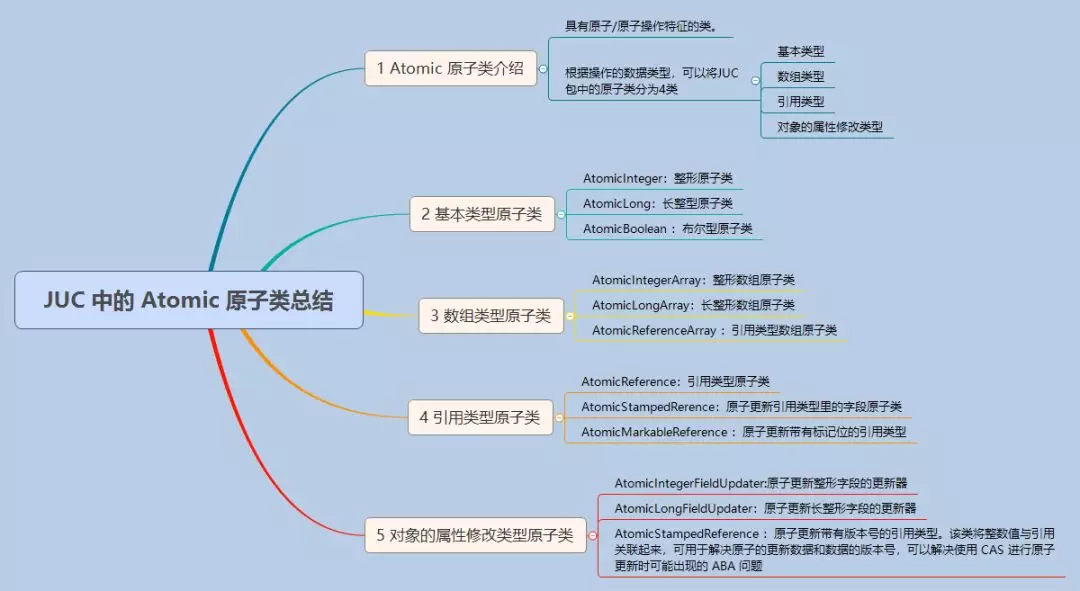
#简介
Atomic原子类位于并发包java.util.concurrent下的java.util.concurrent.Atomic中。
#原子更新基本类型类
使用原子方式更新基本数据类型,Atomic提供以下3个类
- AtomicInteger:原子更新整型
- AtomicBoolean:原子更新布尔型
- AtomicLong:原子更新长整型
以AtomicInteger为例进行介绍:
// 获取index = i位置元素的值
public final int get(int i)
// 返回index = i位置的当前的值,并将其设置为新值newValue
public final int getAndSet(int i, int newValue)
// 获取index = i位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自增
public final int getAndIncrement(int i)
// 获取index = i位置元素的值,并让该位置的元素自减
public final int getAndDecrement(int i)
// 获取index = i位置元素的值,并加上预期的值
public final int getAndAdd(int delta)
// CAS操作,返回是否操作成功
boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update)
//最终将index = i位置元素设置为newValue,使用lazySet可能导致其他线程在之后一小段时间仍可读取旧值。
public final void lazySet(int i, int newValue)
Demo:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class AtomicIntegerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int tempValue = 0;
AtomicInteger i = new AtomicInteger(0);
tempValue = i.getAndSet(3);
System.out.println("先获取当前值后设置新值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 0 3
tempValue = i.getAndIncrement();
System.out.println("先获取当前值后使当前值自增");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 3 4
tempValue = i.incrementAndGet();
System.out.println("先使当前值自增后获取值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 5 5
tempValue = i.getAndAdd(5);
System.out.println("先获取当前值再使当前值加上一个值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 5 10
}
}
AtomicInteger能够解决volatile关键字在面对count++操作时不能保证原子性的问题。使用AtomicInteger后,不需要加锁也可以保证线程安全。
-
多线程环境下采用synchronized关键字加锁保证线程安全
class test01 { private volatile int count = 0; public synchronized void increment() { count++; } public int getCount() { return count; } } -
多线程环境下采用AtomicInteger原子类保证线程安全(无需加锁)
class test02 { private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); public void increment() { count++; } public int getCount() { return count.get(); } }AtomicInteger 类主要利用 CAS (compare and swap) + volatile 和 native 方法来保证原子操作,从而避免 synchronized 的高开销,执行效率大为提升。
#原子更新数组类型类
通过原子方式更新数组里的某个元素,Atomic包提供了以下类:
- AtomicIntegerArray:原子更新整型数组
- AtomicLongArray:原子更新长整型数组
- AtomicReferenceArray:原子更新引用类型数组
以AtomicIntegerArray为例进行介绍:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
public class AtomicIntegerArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int tempValue = 0;
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
AtomicIntegerArray i = new AtomicIntegerArray(arr);
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
System.out.print(i.get(j) + " "); // 1 2 3 4 5
}
System.out.println();
tempValue = i.getAndSet(0, 2);
System.out.println("先获取索引处的当前值后设置新值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 1 [2, 2, 3, 4, 5]
tempValue = i.getAndIncrement(0);
System.out.println("先获取索引处的当前值后使当前值自增");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 2 [3, 2, 3, 4, 5]
tempValue = i.incrementAndGet(0);
System.out.println("先使索引处的当前值自增后获取值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 4 [4, 2, 3, 4, 5]
tempValue = i.getAndAdd(0, 5);
System.out.println("先获取索引处的当前值再使当前值加上一个值");
System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + "; i = " + i); // 4 [9, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
}
#原子更新引用类型类
如果需要原子更新多个变量,就需要使用这个原子更新引用类型提供的类:
- AtomicReference:原子更新引用类型
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:原子更新引用类型里的字段
- AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新打游标记位的引用类型
Demo:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class AtomicReferenceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicReference<User> atomicUserRef = new AtomicReference<>();
User user = new User("AAA", 10);
atomicUserRef.set(user);
User updateUser = new User("BBB", 20);
// 调用CAS方法
atomicUserRef.compareAndSet(user, updateUser);
// 调用get方法并获取姓名和年龄打印
System.out.println(atomicUserRef.get().getName()); // BBB
System.out.println(atomicUserRef.get().getAge()); // 20
}
/**
* 静态内部类User
*/
static class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
}
#原子更新字段类
需要原子更新某个类中的对象属性时,需要使用原子更新字段类:
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新整型字段的更新器
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新长整型字段的更新器
- AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型(解决ABA问题)
要想原子更新对象的属性需要两步:
- 因为原子更新字段类都是抽象类,所以每次使用时都必须使用静态方法
new Updater()创建一个更新器,并且需要设置想要更新的类和属性; - 更新的对象属性必须使用
public volatile修饰。
Demo:
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用newUpdater()方法创建更新器
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<User> a = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(User.class, "age");
User user = new User("AAA", 10);
System.out.println(a.getAndIncrement(user)); // 10
System.out.println(a.get(user)); // 11
}
/**
* 静态内部类User
* 要更新的字段采用public volatile修饰
*/
static class User {
private String name;
public volatile int age;
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}
}